What is the true value of something? If we own a house – for example - the value is what other people are willing to pay for the property. This is set by the market (the number of potential buyers and the number of other homes available for sale). If the price is too high, there will be no potential buyers and it will not sell. But if the price is set too low, although it may sell quickly, it will be sold for less than its worth.
But we can take other things too, what is the value of a gold ring? Sadly, right now, if it has not been made by a well-known jeweller or is not a very unique piece artistically, it is not worth much more than the value of the gold it contains.
Items can also lose value over time as a result of wear and tear or new and better technologies. Computers and phones are a great example of this. Buy a $1000 smartphone today, in 10 years’ time it will be practically worthless.
But what exactly creates the value behind the money in our pockets or the cryptocurrencies in our digital wallets? And, should this change?
How Regular Currencies Used to Have Value?
Before money, all goods were bartered – simply one item swapped for another. You have 10 bags of grain, I will swap this for one sheep. The value of the items exchanged matched the value both parties saw in the goods they were exchanging. But what happened if the other person did not have something you wanted or the value of their goods was not quite enough to meet you own.
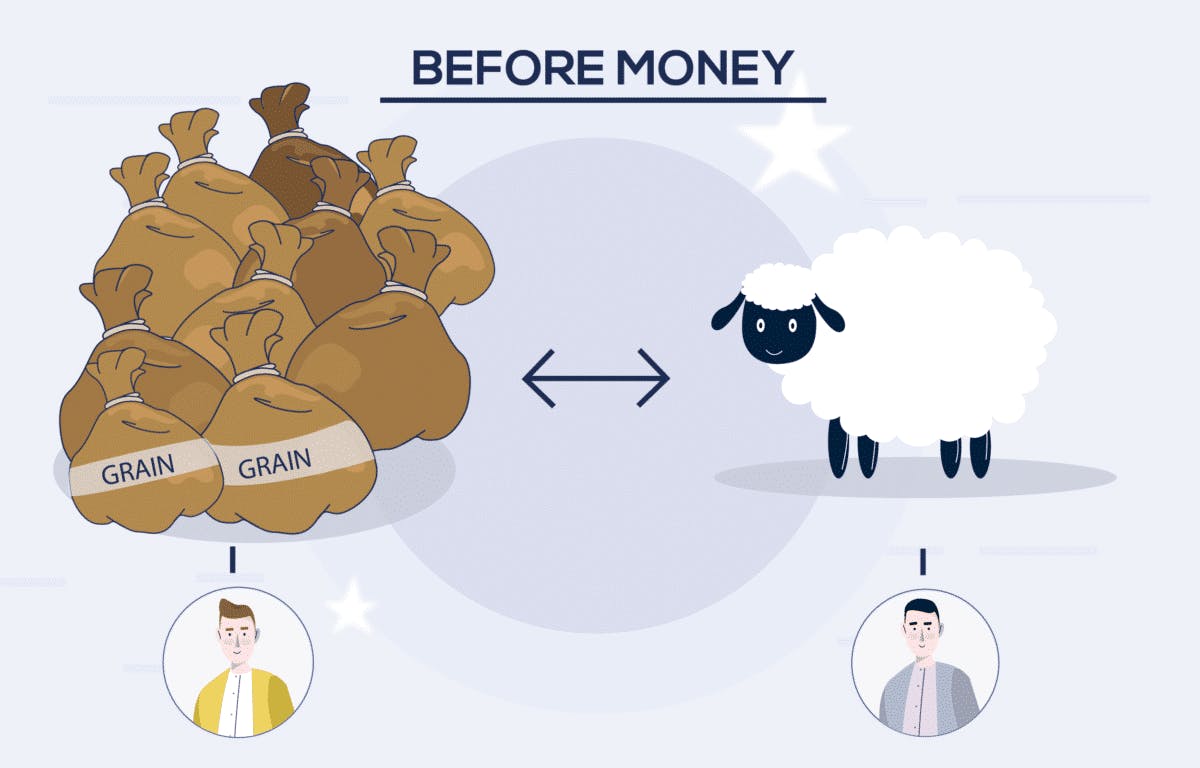
It was for these reasons that metal coins – what we would call money today – began to enter circulation around 7000 years ago. This money, gained its value from the material it was made of, a gold coin obviously being more valuable than a silver, bronze, or even copper coin. At this point, all objects could be given a price, 1 bag of grain = 1 gold coin, 1 sheep = 10 gold coins - for example.
This value of a coin based on the precious metal it was made from remained the standard for approximately 6000 years, before the Chinese began to introduce the first paper money around 900AD. This worked on the premise that paper or non-precious metal coins provided by a bank or government could be exchanged for a certain amount of a precious metal if the holder of the money wished. For example, one British Pound used to be exchangeable for approximately 450g of silver.
How They Have Value Today
However, today, no major currency in the world bases its value on an exchangeable weight of gold, silver or any other metal. The problem with this was that no country could increase how much money was in circulation without also increasing the amount of gold, silver, etc., that it held in its reserves.
Because only a small amount of new gold – for example - is found each year, this meant that inflation would always remain low. However, inflation is needed in a growing economy and is an indicator of increasing prosperity. This is why over the course of the last century governments dropped this standard in exchange for what we call money today – what is known as fiat currency.
A fiat currency creates its value based on how much of the currency is in circulation, the amount of people who are using it, as well as the health of the national economy it is from. This kind of currency gives governments more options. For example, when we look back at the financial crisis 10 years ago, governments were able to print more money. This meant that there was more money in the system that could be lent out to both individuals and businesses who could use this to buy goods or services, hire more workers or expand operations. The aim being to stimulate growth.
The size of the economy also has an impact on both the value and stability of a currency. The larger the economy and country, the more stable it is. For example the Euro is more stable and valuable than the individual currencies of the countries of the union that it replaced. For example, as the Greek economy collapsed a few years ago, the Euro remained stable. Whereas, if this had happened when the Greek Drachma was still in use, this would have seen a fall in the value of the currency and economy of the nation.
What Should The Value of Cryptocurrencies Be Based On?
As cryptocurrencies are virtual, they cannot be made of a precious metal. At the same time, for any individual or group creating a new coin, to obtain enough gold, silver, or any other precious metal, to potentially hold in reserve to back the value of a coin, would just be too expensive and impractical.
We also have to understand that with cryptos, there is no bank or government in control of them and that almost all of them have a fixed number of coins in circulation or that can be mined. For this reason, no additional coins can be created to stimulate an economy during a downturn or even be taken away when inflation is too high.
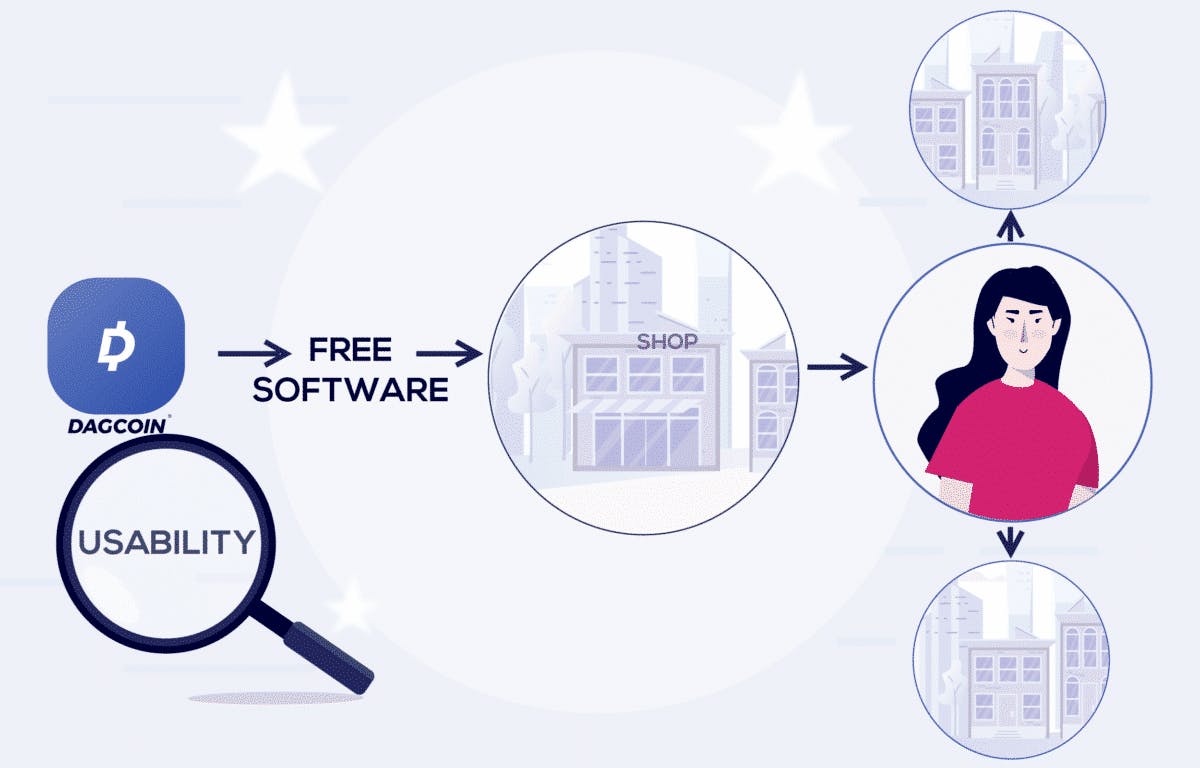
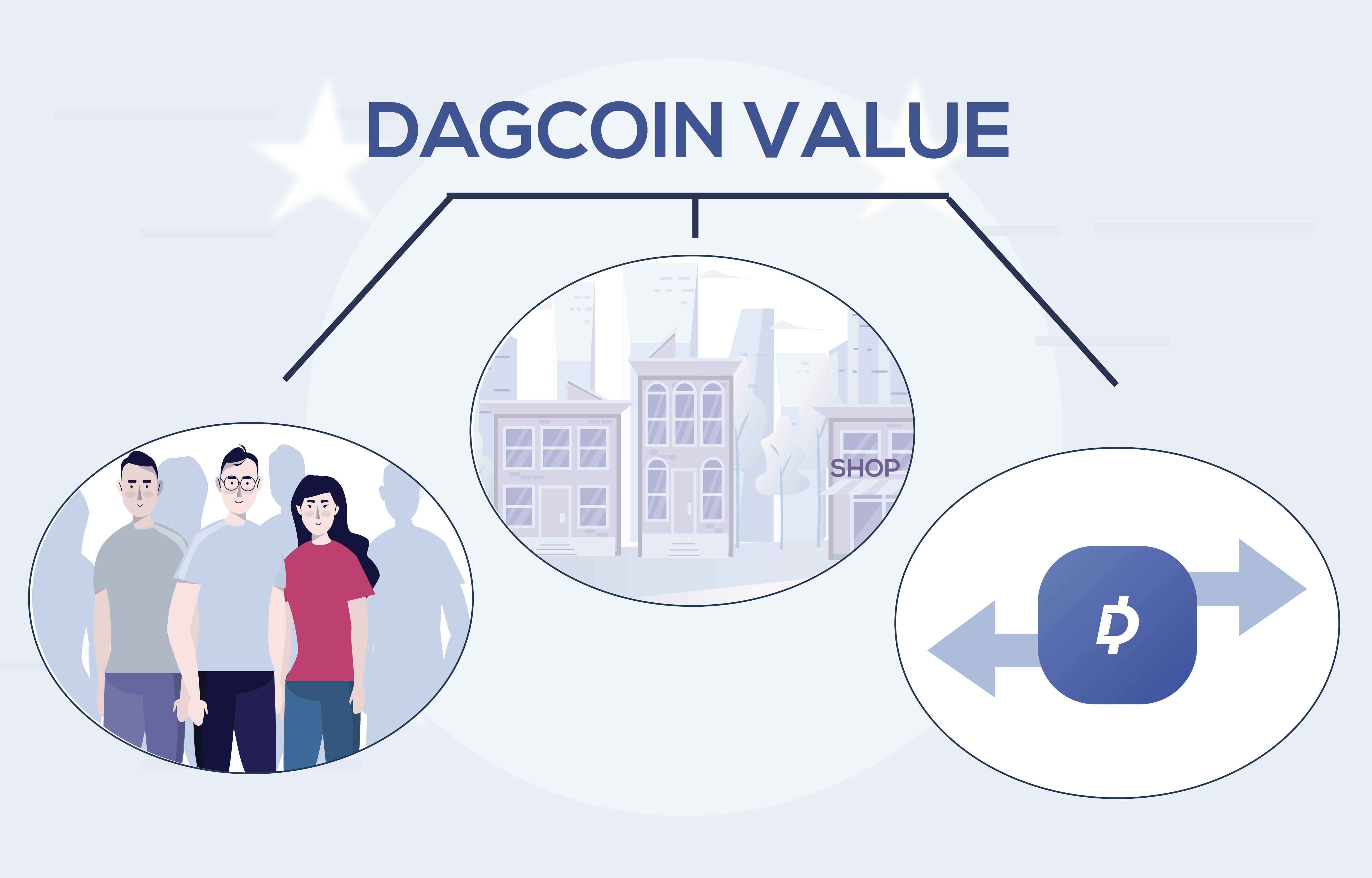
All this means that the value of a cryptocurrency can only realistically be based on the size of the community using it, the number of businesses who accept and the number of transactions that take place each day using it.
This is why Dagcoin has been created with a focus on usability. This has been done by creating a free suite of software to make it easy for businesses to start accepting Dagcoin. This software attracts merchants, which attracts users, which in turn attracts more merchants, and so on. So far Dagcoin has grown to over 300,000 users and 700 merchants worldwide. This focus on usability also means that Dagcoin cannot be traded and is found on no such exchange for that reason.
Once the community is huge, Dagcoin will be valued by the laws of supply and demand. This will happen when the usability has reached levels that the price of Dagcoin is not influenced by trading.
Conclusion
The value of money has changed a lot over time. The first coins gained their value from the precious metals they were made from. This changed to paper and non-precious metal coins that were issued with a promise from a bank or government that they could be exchanged for a certain amount of gold, silver, etc.
Today, money gains its value from the government of the nation that controls it, the number of people using the currency and the state of the national economy. People have trust in the currency and trading does not influence the everyday price of it. Cryptocurrencies cannot gain their value in the same way in the beginning, therefore the value must be first based on:
- The number of people using the coin
- The number of businesses who accept the coin
- The number of daily transactions using the coin
Become part of a community of more than 300,000 people using Dagcoin.